This article is a presentation of a new little framework, I have developed and used on several projects.
The framework is for Spring Framework and requires Java 8.0. The code is on GitHub and downloadable from Bintray or JCenter.
spring-cqrs-arch
Purpose
This module is an implementation of a software architecture model inspired by the CQRS ( link from Fowler ) model.
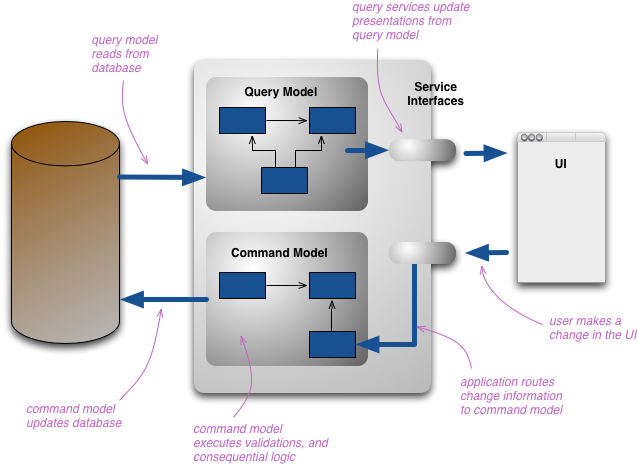
CQRS Architecture
The idea is the following: the software functionalities are split between the reading and the write accesses made by the user.
Advantages
The strongest advantages of this architecture are – according to my experience – :
- Evolutive architecture: this software architecture model enforces several OOP architecture principles (design patterns, transverse functionalities)
- Easy testing: the module and the architecture allows the developer to do unit-testing or component-based testing of its code. Furthermore, this implementation is also providing out of the box: logging, profiling, and tracing (file export) to push the debugging further
- Spring compatible: this architecture is compatible with IOC, Java, and Spring
- Microservice compatible: this module can be used to implement a monolith and split it as microservices later, or directly as microservices if you implement a Bus.
Cleancode
Some bad smells often found in Spring / Java Web applications are avoided with this model.
For instance : * God / Mother classes: Some years ago, it was quite common to find Java classes also known as Services containing quite a bunch of methods, a big grape of autowired services, and poorly tested. These classes were highly fragile, hard to mock and test. By creating a class per command and therefore by use-case, the java classes are fine-grained, easier to mock and test. * Excessive parameters The developer has to encapsulate the data into a Command object to pass it through the gate. This way, the OOP is enforced into the Core of this model.
The implementation model for a web application using CQRS principles.
Scope
This module is offering basically the Command architecture principles, and a way to send events.
For the query part, I recommend a progressive approach :
- Use the same database and the same database access technology (with ORM)
- Use another database access technology (without ORM or NoSQL)

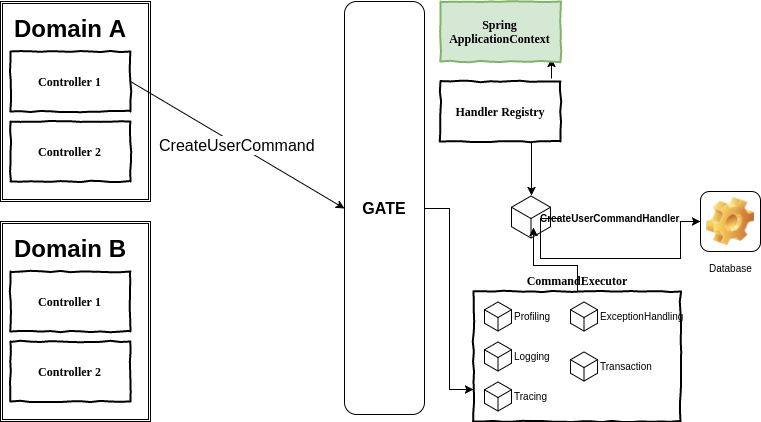
Module architecture design
How to use
Configuration
The module requires defining a Bean to start it (CqrsConfiguration).
The easiest way is to create a Configuration bean and to declare the configuration inside :
@Configuration
public class CqrsModuleConfiguration {
public CqrsConfiguration configure() {
CqrsConfiguration configuration = new CqrsConfiguration();
// Configure there
return configuration;
}
}How to begin
To conceive an application using CQRS, you need to think that way :
- What are my use cases: define your use-cases expressed as operation s(READ or Write) or eventually a sequence flow diagram per use-case
- Distinguish your write access: for example, create a new user, edit his phone number. Avoid as much as possible generic and poor business meaning operations as CRUD (Create, Update, Delete). Think about what are you trying to update? His personal details? Are you toggling the email configuration flag? Obviously, all these operations are a writer and could be written as a big Update method. CQRS is enforcing the DDD approach. Meaning is a rule to write better application toward functional design rather than technical design and to increase productivity.
- Start by writing your commands: that is the easiest part :
Write a command
A command is a basic Pojo :
public class CreateUserCommand {
public String email;
public String password;
}Every command is tested using the Validation API and usually the Hibernate validator API.
public class CreateUserCommand {
@NonEmpty
@Email
public String email;
@NonEmpty
@Size(minimum=8)
public String password;
}It means the gate will validate the command before executing them.
If you pay attention, you should be able to convert your request body or payload directly as a Command.
Send the command
To send a command, you need to send the object through the gate.
To do so, inject the Gate dependency with @Autowired
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private Gate gate;
}You have two possibilities to send a command :
- a direct way :
gate.dispatch(command); - an asynchronous way :
gate.dispatchAsync(command);
The methods are returning the results of the command execution.
Write a command handler
To write a command handler, you need to implement a Spring bean defining the interface ICommandHandler.
The interface ICommandHandler is taking two type parameters : * the first one is the command handled: example CreateNewCommand * the second is the returned type of the command handler: the result produced by the execution of the command.
example :
@CommandHandler
public class CreateNewUserCommandHandler implements ICommandHandler<CreateNewUserCommand, Integer> {
@Override
public Integer handle(final CreateNwUserCommand command) throws Exception {
return 1;
}
}We also recommend sending events to notify the change in the repository. The gate is offering such a proxy. The default event bus is in Guava but can be implemented using the Spring applicationEvent or more complex implementations.
@CommandHandler
public class CreateNewUserCommandHandler implements ICommandHandler<CreateNewUserCommand, Integer> {
@Autowired
private Gate gate;
@Override
public Integer handle(final CreateNewUserCommand command) throws Exception {
gate.dispatchEvent(new EventNewUserCreated());
return 1;
}
}Spring Profiles
Here are the following profiles to enable features in the module :
@Profile("guava_bus")Exception Handling
Here is the list of Exception that may be thrown by the CQRS Gate :
CommandExecutionException.java: When the execution has failed, the default exception handler is wrapping the checked exception in this exception.CommandHandlerNotFoundException.java: When a command is sent through the gate but no handler has been found.CqrsException.java: Base exception classInvalidCommandException.java: Commands are validated using the JEE API validation. If an invalid command has been sent to the Gate, the Exception will be returned. The exception encloses a ConstraintsViolationException with the list of invalid properties.
The gate is provided with a default Exception handler with the following behavior:
- Any caught exception is wrapped inside a CommandExecutionException.
The behavior can be changed using your own ICommandExceptionHandler.
Listener on command execution
It is possible to implement a listener (or many) to trap the execution of a command through the gate.
To do so, simply implement a new Spring bean implementing the interface ICommandExecutionListener.
@Bean
public class DemoBean implements ICommandExecutionListener {
}Transactions
The transaction can be implemented in two ways :
- Creating an ICommandExecutionListener and trigger the transaction as a wrapper over the execution of a transaction
- Directly on the CommandHandler by adding the appropriate @Transaction